-
White storks make strong return in France via nest ‘platforms’ and clipped wings
The Ligue pour la Protection des Oiseaux shares the conservation challenges in saving these birds from extinction
-
Hosting scheme in south-west France lets newcomers sample lifestyle
Households in nine Dordogne communes volunteer under Mes Nouveaux Voisins scheme
-
French boulangeries demand right for staff to work on May 1 so they can open
Artisan bakery owners can work but employees cannot, while certain industrial bakeries are allowed to remain open with workers
MAP: Air pollution in France, the worst - and best - areas
Cities and the countryside face different threats

Wine growers, wood stoves, pig farms and aluminium works are just some of the vectors of air pollution in France. We look at the various health risks the country is facing in different regions.
Results from 2022 placed France in the bottom tier for pollution in Europe, alongside Italy, Bulgaria and Greece. That year, 25 local authorities in France exceeded the European safety thresholds for major pollutants.
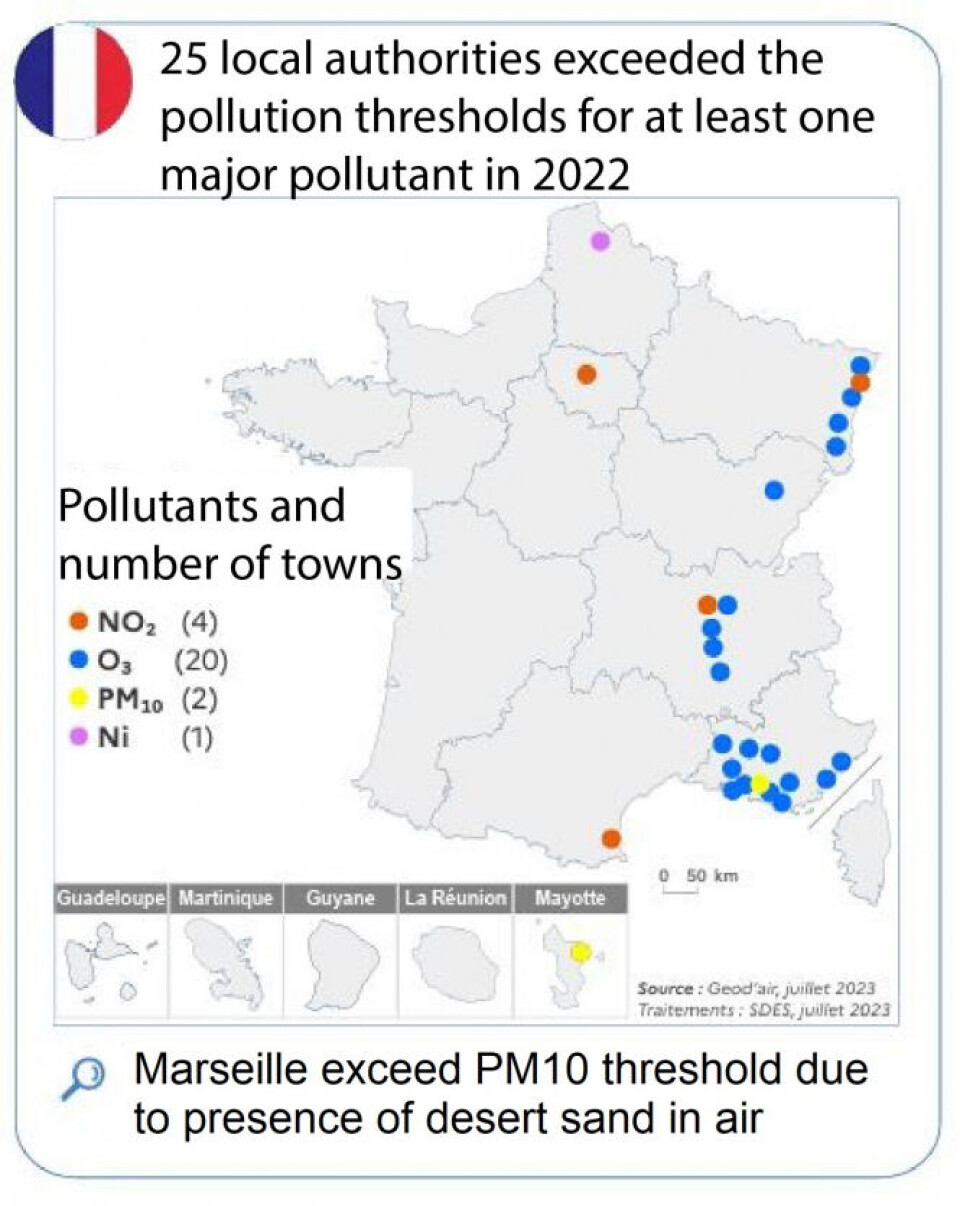
Credit: statistiques.developpement-durable.gouv.fr
However, pollution is by no means running wild in France, indeed pollutants are typically limited to certain sectors of activity, in which their use is restricted.
Some examples of this would be the plan Ecophyto rules against pesticide use in farming, or the Crit’air car stickers on vehicles in city centres.
Both schemes were created to address specific problems and both have faced a backlash: a petition calling for the ban of Crit’air stickers gathered almost 265,000 signatures, while the right to use pesticides was one of the key demands during the farmers’ protests in February 2024.
What are the main forms of pollution in France?

Credit: notre-environnement.gouv.fr
The main pollutant in residential areas is ‘particulate matter’ (PM2.5 and PM10), which are made by burning wood and coal. Both PM2.5 and PM10 cause respiratory problems
Read more: Wood burning stoves: what are the rules in France?
Ammonia from fertilisers and animals is the main pollutant in rural areas. This can cause respiratory problems and asthmatic reactions with long-term exposure.
Nickel, which is used in metalworking, is a major pollutant in industrial areas and can cause a wide range of negative health effects, from respiratory problems to cancers.
Read more: Explosion at Dordogne chemical factory: low pollution risk for locals
Which rural areas are most at risk of pollution?
Credit: Solagro
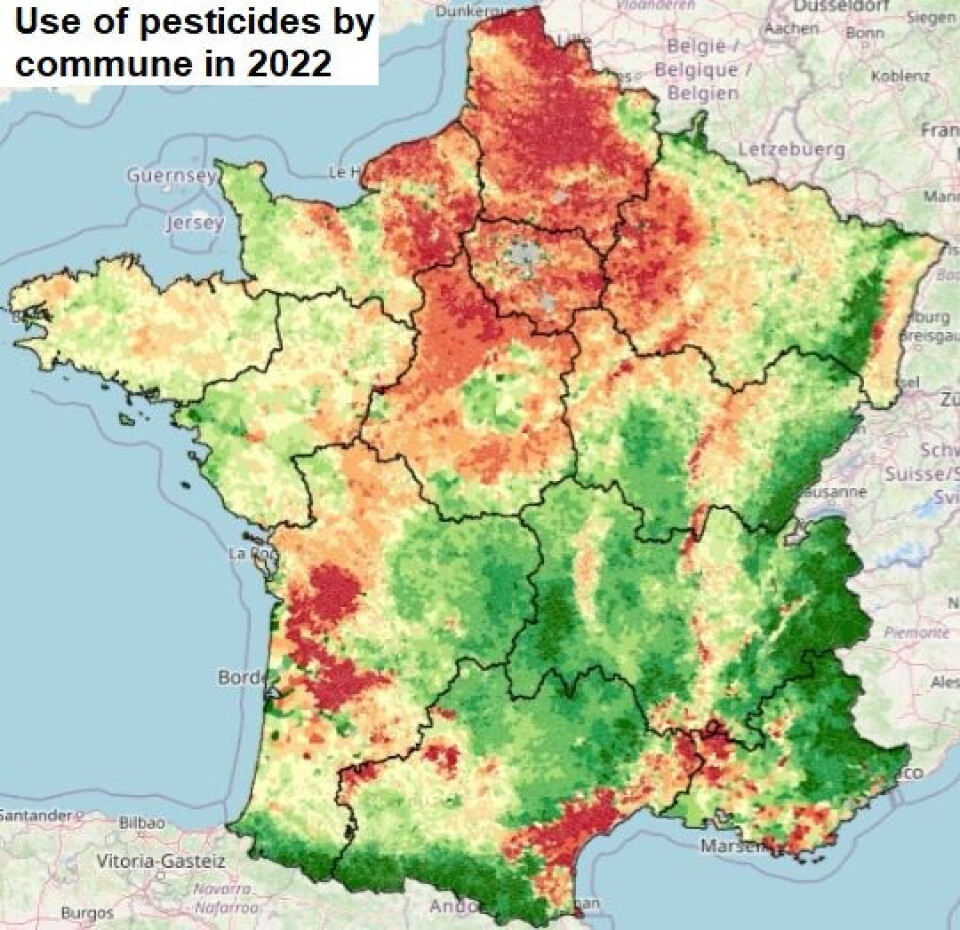
Pesticide use is particularly widespread in the wine growing areas of Bordeaux, Champagne and Occitanie, as well as in the wheat fields of northern France, according to a wide ranging study by the Solagro association, which promotes environmentally friendly agriculture.
Their interactive map, which is searchable by commune, is available here.
Credit: georisques.fr
Ammonia, which is the greatest single rural form of pollution (pesticides come in several forms) disproportionately strikes the Brittany region.
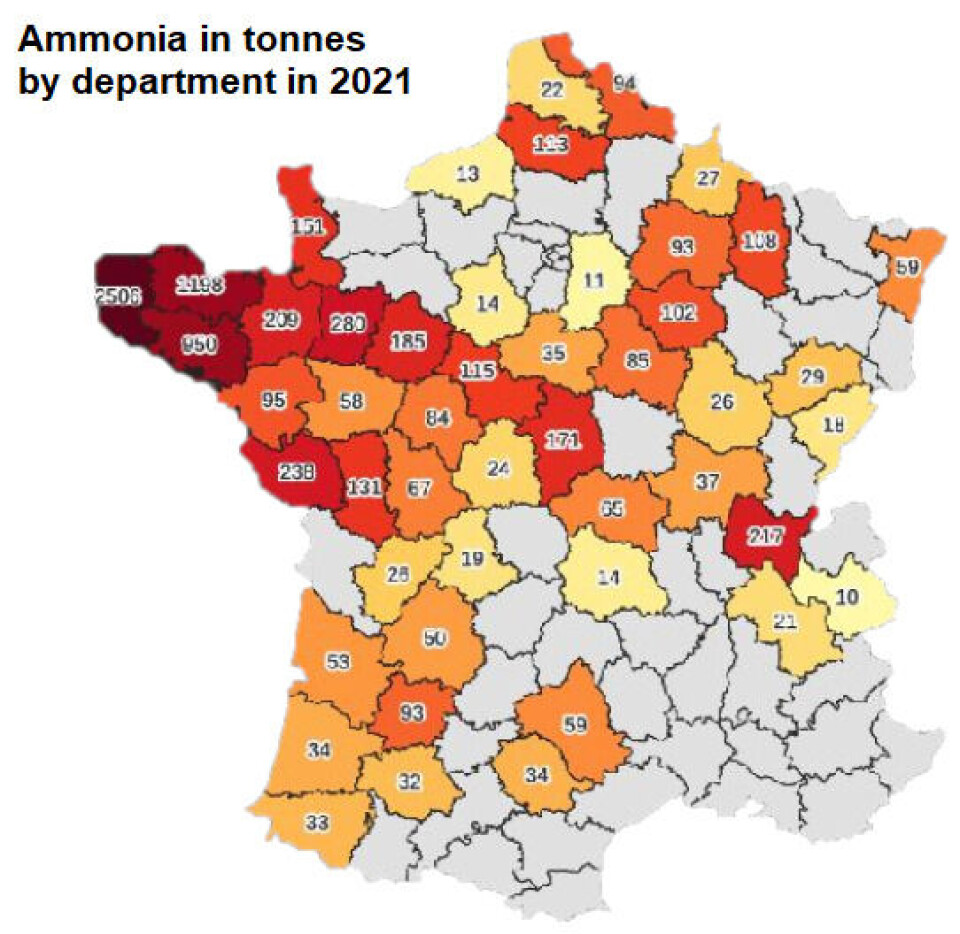
This is largely due to the presence of pig farms: pigs produce ammonia in their urine and faeces.
Daily pollution
Pollution in France has a significant seasonal and meteorological component: it is exasperated by the high summer temperatures and periods of pollen.
Read more: LIST: Calendar of main pollen allergies in France month by month
A map of France’s day-by-day exposure to pollution from NO2, PM2.5, PM10 and Ozone is available here.
Read more
Hope for allergic asthma sufferers as French laboratory tests vaccine
























